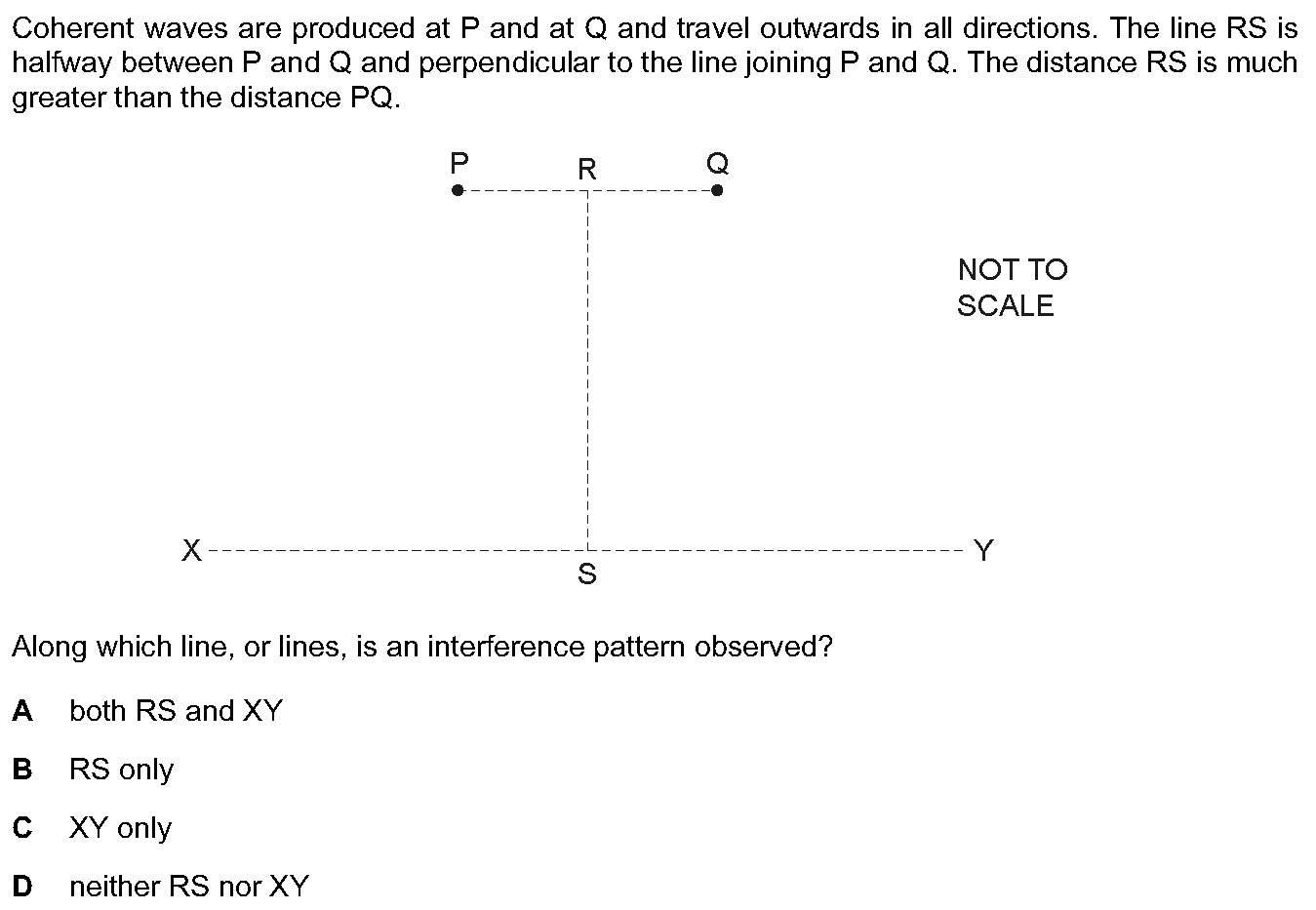
Q30:
AS & A Level Physics - 9702 Paper 1 2011 Winter Zone 1
Questions:
30/40

Topic: CH15 - SUPERPOSITION
Solution
Solution is C,C

PRACTISE
Similar Questions

LEARN
Concepts with Sparky

More Questions from this Topic
MCQ
CH15 - SUPERPOSITION
A loudspeaker is playing music in a room. The door to the room is open and has a width of 0.80 m.
Sound waves of many different frequencies pass thro...
2024
 Summer
Summer
 Summer
Summer
 6
6
MCQ
CH15 - SUPERPOSITION
A stationary sound wave is set up between a loudspeaker and a wall.
A microphone is connected to a cathode-ray oscilloscope (CRO) and is moved along ...
2024
 Summer
Summer
 Summer
Summer
 4
4
MCQ
CH15 - SUPERPOSITION
For a wire, Hooke's law is obeyed for a tension $F$ and extension $x$. The Young modulus for the material of the wire is $E$.
Which expression repres...
2024
 Summer
Summer
 Summer
Summer
 5
5
MCQ
CH15 - SUPERPOSITION
A guitar string is plucked. Which statement describes the resulting waves?
2024
 Summer
Summer
 Summer
Summer
 6
6
MCQ
CH15 - SUPERPOSITION
A plane polarised wave has amplitude $A$. The wave is incident normally on a polarising filter.
The transmission axis of the filter is at angle $\the...
2024
 Summer
Summer
 Summer
Summer
 5
5
MCQ
CH15 - SUPERPOSITION
A stationary sound wave is formed in the air column inside a tube that is open at both ends.
The stationary wave has three nodes.
How many antinodes...
2024
 Summer
Summer
 Summer
Summer
 7
7
MCQ
CH15 - SUPERPOSITION
Light of frequency $6.7 \times 10^{14}\, \text{Hz}$ in a vacuum is incident normally on a diffraction grating that contains $4.0 \times 10^{5}\, \text...
2024
 Summer
Summer
 Summer
Summer
 4
4
MCQ
CH15 - SUPERPOSITION
The siren of a moving police car emits a sound wave with a frequency of 440 Hz. A stationary observer hears sound of frequency 494 Hz. The speed of so...
2024
 Summer
Summer
 Summer
Summer
 3
3
MCQ
CH15 - SUPERPOSITION
What happens when two waves superpose at a point?
2024
 Winter
Winter
 Winter
Winter
 5
5
MCQ
CH15 - SUPERPOSITION
Waves P and Q have the same amplitude. The waves meet in phase at point X and interfere to give a resultant wave with intensity $I$.
The amplitude of...
2024
 Winter
Winter
 Winter
Winter
 4
4
More Questions from year 2011
Theory
CH2 - MEASUREMENT TECHNIQUES
Measurements made for a sample of metal wire are shown in Fig. 1.1.
Fig. 1.1
(a) State the appropriate instruments used to make each of these meas...
2011
 Summer
Summer
 Summer
Summer
 3
3
Theory
Kinetic Energy
(a) Explain what is meant by work done. [1]
(b) A car is travelling along a road that has a uniform downhill gradient, as shown in Fig. 2.1.
...
2011
 Summer
Summer
 Summer
Summer
 4
4
Theory
CH5 - FORCES, DENSITY & PRESSURE
(a) Explain what is meant by centre of gravity.
(b) Define moment of a force.
(c) A student is being weighed. The student, of weight $W$, stands 0.3...
2011
 Summer
Summer
 Summer
Summer
 6
6
Theory
CH9 - DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS
(a) Define, for a wire,
(i) stress, [1]
(ii) strain. [1]
(b) A wire of length 1.70 m hangs vertically from a fixed point,...
2011
 Summer
Summer
 Summer
Summer
 3
3
Theory
CH20 - D.C. CIRCUITS
(a) A variable resistor is used to control the current in a circuit, as shown in Fig. 5.1. The variable resistor is connected in series with a 12V po...
2011
 Summer
Summer
 Summer
Summer
 2
2
Theory
CH5 - FORCES, DENSITY & PRESSURE
(a) State two assumptions of the simple kinetic model of a gas. [2]
(b) Use the kinetic model of gases and Newton's laws of motion to exp...
2011
 Summer
Summer
 Summer
Summer
 3
3
Theory
CH15 - SUPERPOSITION
(a) Explain the term interference. [1]
(b) A ripple tank is used to demonstrate interference between water waves.
Describe
(i) the appa...
2011
 Summer
Summer
 Summer
Summer
 2
2
Theory
CH1 - PHYSICAL QUANTITIES & UNITS
(a) Distinguish between scalar quantities and vector quantities. [2]
(b) In the following list, underline all the scalar quantities.
accelerati...
2011
 Summer
Summer
 Summer
Summer
 5
5
Theory
CH1 - PHYSICAL QUANTITIES & UNITS
(a) A sphere of radius $R$ is moving through a fluid with constant speed $v$. There is a frictional force $F$ acting on the sphere, which is given by ...
2011
 Summer
Summer
 Summer
Summer
 2
2
Theory
Potential Energy
(a) (i) Explain what is meant by work done. [1]
(ii) Define power. [1]
(b) Fig. 3.1 shows part of a fairground ride with a carriage on rai...
2011
 Summer
Summer
 Summer
Summer
 2
2




 Share
Share




 Previous
Previous